Management of Balance and Movement Disorder
CP Management approaches to improve mobility and self-care:
- Physiotherapy - is a cornerstone of CP treatment, using a manual, hands-on approach with soft tissue and fascial releases, stretches, and massages, to maintain or improve muscle strength, balance, and motor skills, and prevent contractures. Special braces (orthotic devices) may be used to improve mobility and stretch spastic muscles (NINDS, 2023).
- Occupational therapy – focuses on optimizing upper body function, improving posture, and making the most of a child's mobility. Occupational therapists help individuals adapt everyday items, activities, routines and assistive devices at home, school, and in the community (NINDS, 2023).
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy - controversial treatment intended to stimulate and recruit nerve cells in the areas of central neurologic impairment by breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment.
- Sensory integration – helps with processing information received from our 5 senses, organizing it, and responding appropriately.
- Hippotherapy - an approach to PT and OT where the patient rides horses in order to address physical health
- CIMT – constraint-induced movement therapy may be considered to focus functioning of an affected extremity by restricting the use of the uneffected limb (Ramsey, 2021).
- BWSTT – body weight supported treadmill training.
- Acupuncture is the practice of penetrating the skin with needles activated by hand movements or electrical stimulation.
- Vojta method - reflex locomotion involving reflex crawling and reflex rolling designed to trigger these motor patterns (Upadhyay et al., 2020).
Here are some more recent treatment techniques:
- Whole-body vibration and core stability exercises, with the former being more effective (Ali et al., 2019).
- Virtual reality, given 20 minutes twice a week for 6 weeks, leads to improvement (Montoro-Cardenas et al., 2021).
- Nintendo Wii therapy is used to improve functional and dynamic balance in combination with physiotherapy (Montoro-Cardenas et al., 2021)
Management of Hip, Knee and Ankle Deformities
Hip
- The hip joints of children with CP may be normal at birth (Miller F., 2017).
- Hip disorders develop in about 33% of children with CP (Miller S,. 2019).
- Asymmetric tightening and spasticity of the muscles in the upper leg and around the joint slowly displace the femoral head lateral and posterior superior.
- These disorders can lead to subluxation/dislocation. Untreated dislocation can lead to degenerative arthritis and intractable pain.
- The subluxation process begins around 2 years old and progresses about one degree per month (Miller F., 2017).
- Screening radiographs should begin around age 2 year. The highest risk for developing subluxation/dislocation occurs in children who cannot walk or require the use of an assistive device.
Surgical Treatment for spastic hip dislocation -
- Preventative surgery to reduce the risk of hip dislocation caused by spastic hip adductor muscles may benefit from adductor muscle lengthening.
- Surgical intervention may be considered when abduction is reduced with the subluxation migration percentage reaches 25 to 40% (Miller F., 2017).
- Reconstructive surgeries for early hip displacement deformities are intended to realign the femoral head to relocate it into the acetabular socket.
- Varus derotation osteotomy (VDRO)
- Pelvic osteotomy - cutting and repositioning the pelvic bone to improve the alignment of the hip joint and provide better coverage of the femoral head by the acetabulum.
- Post surgical: immobilization with Spica cast for 4-6 weeks, rehabilitation, abduction brace when napping and night-time (Park, et al. 2020).
Knee
- Nonoperative interventions for hamstring contracture may include
- Stretching
- Night-time knee immobilizer
- hamstring botulinum toxin A injection (Themes, 2016).
- Surgical intervention
- Hamstring Lengthenings may be indicated for children with excessive knee flexion in gait swing and stance (Themes, 2016).
- Anterior Hemiepiphysiodesis of the Distal Femur for children >2 with significant crouch, knee flexion contracture of > 15 to 25 degrees (Themes, 2016).
- Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy (with Patellar Tendon Advancement) for adolescents with significant crouch, knee flexion contracture of 15 degrees (Themes, 2016)
- Distal Rectus Femoris Transfer indicated for patients with stiff knee swing phase of gait and overactive rectus femoris in swing (Themes, 2016).
Ankle/foot disorders
- Flat feet
- Clubfoot
- Toe walking
Nonsurgical treatments
- Physical therapy, calf stretches, foot extension stretch
- Bracing, casting, night splints
- Heel Lifts
- Orthotic devices, include types of AFOs (Ankle-Foot-Orthotics and/or the Hkafo (Hip-KneeAFOs) can improve ankle range, joint function, and gait parameters and reduce the child’s energy expenditure. (https://www.cerebralpalsy.org/information/mobility/orthotics)
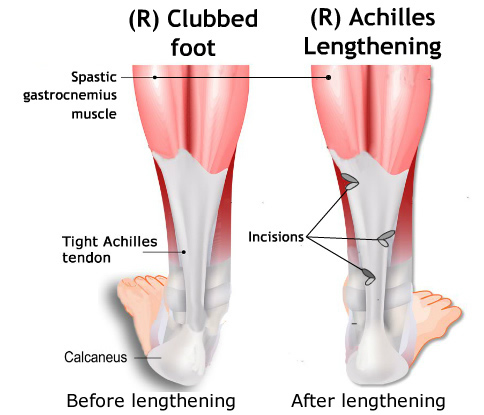 Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment
- Tendon lengthening
- Achilles tendon lengthening
- Tendon tranfer changes the position of tendon attachment which alters the direction and force of muscular contraction applied to the affected joint.
- Reconstructive osteotomy and fixation to realign boney deformities
- Joint fusion
Instant Feedback:
What is the therapeutic intervention called that helps with processing information received from our 5 senses, organizing it, and responding appropriately?
References
Ali, M., Awad, A. & Elassal, P. (2019). The effect of two therapeutic interventions on balance in children with spastic cerebral palsy: a comparative study. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences. 14(4),350–356.
Miller, F. (2017). Natural History and Surveillance of Hip Dysplasia in Cerebral Palsy. In: Miller, F., Bachrach, S., Lennon, N., O'Neil, M. (eds) Cerebral Palsy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50592-3_126-1
Miller, S. D., Shore, B. J., & Mulpuri, K. (2019). Hip Surveillance is Important to Children with Cerebral Palsy: Stop Waiting, Start Now. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Global research & reviews, 3(4), e021. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-19-00021
Li, L.X., Zhang, M.M., Zhang, Y. & He, J. (2018). Acupuncture for cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neural Regen Res. 13(6), 1107-1117.
Montoro-Cárdenas, D., Cortés-Pérez, I., Zagalaz-Anula, N., Osuna-Pérez, M. C., Obrero-Gaitán, E. & Lomas-Vega, R. (2021). Nintendo Wii balance board therapy for postural control in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology . 63(11), 1262–1275.
Cerebral palsy. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS 2023). https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/cerebral-palsy
Paul, S., Nahar, A., Bhagawati, M. & Kunwar, A.J. (2022). A Review on Recent Advances of Cerebral Palsy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 30;2022:2622310.
Park, H., Abdel-Baki, S. W., Park, K. B., Park, B. K., Rhee, I., Hong, S. P., & Kim, H. W. (2020). Outcome of Femoral Varus Derotational Osteotomy for the Spastic Hip Displacement: Implication for the Indication of Concomitant Pelvic Osteotomy. Journal of clinical medicine, 9(1), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010256
Ramey, S. L., DeLuca, S. C., Stevenson, R. D., Conaway, M., Darragh, A. R., & Lo, W. (2021, November 1). Constraint-induced movement therapy for cerebral palsy: A randomized trial. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/148/5/e2020033878/181349/Constraint-Induced-Movement-Therapy-for-Cerebral?autologincheck=redirected
Shore, B. J., & Graham, H. K. (2017). Management of Moderate to Severe Hip Displacement in Nonambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy. JBJS reviews, 5(12), e4. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00027
Themes, U. (2016, June 13). Lower-extremity surgery in children with cerebral palsy. Musculoskeletal Key. https://musculoskeletalkey.com/lower-extremity-surgery-in-children-with-cerebral-palsy/
© RnCeus.com
 Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment